Eco-accommodating Refrigerants
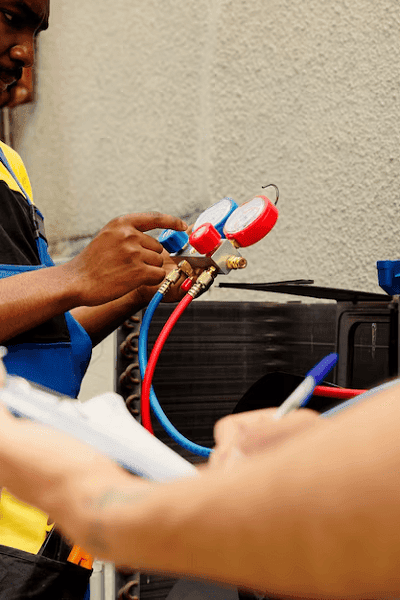
Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? Eco-friendly refrigerants are alternatives to traditional refrigerants that have a lower environmental impact, specifically in relation to global warming potential (GWP) and ozone depletion potential (ODP). These refrigerants are designed to be more sustainable, reducing harmful effects on the environment. Here are a few examples of eco-friendly refrigerants: The key focus for eco-friendly refrigerants is to use substances with minimal or no impact on global warming and ozone depletion, while still maintaining high efficiency and safety standards. Is there a specific type of refrigerant or application you’re particularly interested in? I can provide more detailed info on that! What is Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? Eco-friendly refrigerants refer to refrigerants (the substances used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to transfer heat) that have minimal or no harmful effects on the environment, especially in terms of: Traditional refrigerants, like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), are harmful because they have high ODP and GWP. Over the years, efforts have been made to find better alternatives that reduce these harmful impacts. Types of Eco-friendly Refrigerants: Key Benefits: Overall, eco-friendly refrigerants represent a shift toward reducing the environmental footprint of refrigeration and air conditioning systems, playing a critical role in combating climate change. Would you like more details on a specific eco-friendly refrigerant or how they’re used in particular industries? Who is required Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? Eco-friendly refrigerants are required by various industries, organizations, and governments to reduce environmental impacts such as climate change and ozone depletion. Below are the key groups that are particularly required or incentivized to use these refrigerants: 1. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Industry: 2. Automobile Industry: 3. Governments and Regulatory Bodies: 4. Commercial and Industrial Users: 5. Building Owners and Property Managers: 6. Climate Change and Environmental Advocacy Organizations: 7. Consumers (Indirectly): Why These Groups Are Required to Use Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Conclusion: The requirement for eco-friendly refrigerants spans across several sectors, including the refrigeration and air conditioning industries, automobile manufacturers, governments, commercial enterprises, and even individual consumers. It is a critical move to reduce environmental damage and achieve global sustainability goals. Would you like to know more about the specific laws or regulations in any region or industry? When is required Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? The requirement for eco-friendly refrigerants is largely driven by regulations, international agreements, and industry trends aimed at reducing the environmental impact of refrigerants. The timing of these requirements varies by region, industry, and refrigerant type, but several key deadlines and milestones highlight when eco-friendly refrigerants are becoming necessary: 1. International Agreements and Regulations 2. Automobile Industry 3. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Industry 4. Building and Commercial Sector 5. Deadlines for Compliance 6. Specific Product and System Deadlines: Conclusion Eco-friendly refrigerants are required as part of a global effort to mitigate climate change, protect the ozone layer, and improve energy efficiency. The timing of when these refrigerants become necessary is driven by international agreements, national regulations, and the adoption of greener technologies across industries. Key deadlines for compliance span from 2024 (for developing countries) to 2045 (for full phase-down of HFCs), with industries required to transition progressively in the meantime. Would you like to know more about a specific region’s regulations or a particular industry’s transition timeline? COURTESY : PK Classes Where is required Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? Eco-friendly refrigerants are required in various regions, industries, and applications across the world due to growing environmental concerns and stringent regulations aimed at protecting the climate and ozone layer. Below are the key areas where eco-friendly refrigerants are required: 1. Geographical Regions 1.1 Europe 1.2 United States 1.3 Canada 1.4 Australia and New Zealand 1.5 Developing Countries (Africa, Asia, Latin America) 2. Industries Requiring Eco-friendly Refrigerants 2.1 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Industry 2.2 Automotive Industry 2.3 Building and Construction 2.4 Cold Chain and Food Industry 2.5 Industrial Refrigeration 3. Emerging Trends and Opportunities 3.1 Retrofit and Replacement 3.2 Consumer Products Conclusion Eco-friendly refrigerants are required across various geographical regions and industries, especially in areas with strict regulations focused on climate change, ozone layer protection, and energy efficiency. Key regions requiring these refrigerants include Europe, North America, Australia, and increasingly developing countries under international agreements like the Kigali Amendment. Industries such as refrigeration, automotive, air conditioning, commercial buildings, and cold chain logistics are at the forefront of adopting these refrigerants due to regulatory requirements, energy efficiency goals, and environmental responsibility. Would you like more details about the specific regulations in a particular region or industry? Let me know! How is required Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? The requirement for eco-friendly refrigerants arises from a combination of regulations, industry practices, and global environmental goals. These factors ensure that refrigerants with low or zero Global Warming Potential (GWP) and Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) are used in various applications, replacing older refrigerants with harmful effects. Here’s how these requirements are being implemented and enforced across industries and regions: 1. Regulations and Legislation 1.1 International Agreements 1.2 National Regulations 2. Industry Adoption and Standards 2.1 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (HVAC) 2.2 Automotive Industry 2.3 Cold Chain and Food Industry 2.4 Building and Construction 3. Training, Certification, and Compliance 3.1 Technician Training and Certification 3.2 Monitoring and Enforcement 4. Consumer Awareness and Market Demand Conclusion Eco-friendly refrigerants are required by a combination of regulatory mandates, industry practices, technological advancements, and consumer demand. Governments enforce these requirements through international agreements, national regulations, and industry standards. Businesses are required to transition to eco-friendly refrigerants to comply with these regulations and meet sustainability goals. Furthermore, training programs for technicians and market demand for environmentally responsible products also drive the widespread adoption of these refrigerants. Would you like more details on specific regulations in your region or industry? Feel free to ask! Case study is Eco-accommodating Refrigerants ? Case Study: Adoption of Eco-Friendly Refrigerants in Supermarkets Background: In recent years, supermarkets have become key players in the transition to eco-friendly refrigerants due to their high energy consumption and large refrigeration systems. The food retail sector, including supermarkets, relies heavily on refrigeration to store perishable goods. Historically, this has
Eco-accommodating Refrigerants Read More »