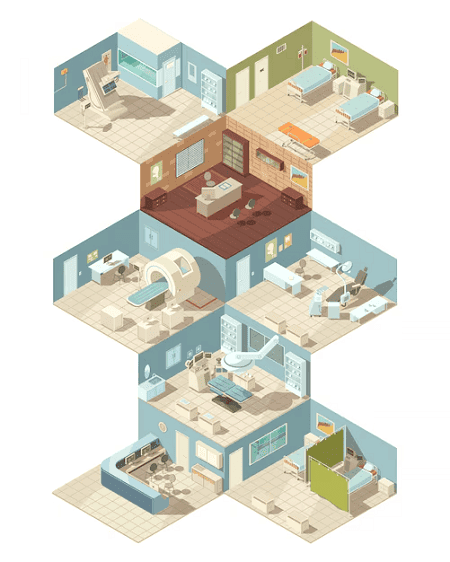
Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities
Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? Healthcare facilities can be broadly classified based on the types of services they offer: Within each of these facility types, spaces can be further classified based on their function: The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is important for several reasons: In addition to the classifications mentioned above, healthcare facilities can also be classified based on their level of care. For example, a primary care clinic provides a different level of care than a tertiary care hospital. The level of care provided by a facility will affect the types of spaces that are needed. Overall, the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is a complex topic. There are many different ways to classify spaces, and the best approach will vary depending on the specific facility. What is Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? Healthcare facilities are complex environments with a variety of spaces designed to support different functions and activities. Classifying these spaces is essential for efficient design, operation, and regulatory compliance. Here’s a breakdown of how spaces in healthcare facilities are classified: 1. Based on Service Type: 2. Based on Function: 3. Based on Level of Care: Importance of Classification: Additional Considerations: Key Standards and Guidelines: In Conclusion: Classifying spaces in healthcare facilities is a multifaceted process that considers various factors, including service type, function, level of care, and specific needs. Effective classification is crucial for creating safe, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare environments. Who is required Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is important for a variety of stakeholders, including: Here are some specific examples of how different stakeholders use the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities: Overall, the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is important for a variety of stakeholders. By understanding the different types of spaces needed, healthcare providers, architects, designers, construction companies, regulatory agencies, and patients can work together to create safe, efficient, and comfortable healthcare environments. When is required Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is required at several key stages: 1. Planning and Design: 2. Regulatory Compliance: 3. Operational Efficiency: 4. Patient Safety: 5. Continuous Improvement: In summary, the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is an ongoing process that starts with planning and design and continues throughout the facility’s lifecycle. It is essential for regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, patient safety, and continuous improvement. COURTESY : Kelli Belanger Where is required Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is required in a variety of settings and contexts, including: 1. Healthcare Facilities Themselves: 2. Design and Construction: 3. Regulatory and Accreditation Bodies: 4. Other Stakeholders: In essence, the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is relevant wherever healthcare services are provided, designed, regulated, or studied. It is a fundamental tool for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and effectiveness of healthcare environments. How is required Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is a structured process that involves several key steps: 1. Identifying the Purpose and Function of Each Space: 2. Applying Relevant Classification Systems: 3. Considering Specific Requirements and Standards: 4. Documenting and Communicating the Classification: 5. Reviewing and Updating the Classification: By following these steps, healthcare facilities can effectively classify their spaces to support efficient operations, patient safety, regulatory compliance, and continuous improvement. Case study is Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? Case Study: Classification of Spaces in a New Outpatient Clinic Scenario: A healthcare provider is building a new outpatient clinic specializing in cardiology. They need to classify the spaces within the clinic to ensure efficient design, regulatory compliance, and patient safety. 1. Identifying Spaces and Functions: The clinic will include: 2. Applying Classification Systems: 3. Considering Requirements and Standards: 4. Documentation and Communication: 5. Review and Updates: Outcome: By classifying spaces effectively, the clinic can: This case study demonstrates the importance and process of classifying spaces in a healthcare facility. It highlights how this process contributes to creating a safe, efficient, and patient-centered environment. COURTESY : Anixter White paper on Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? White Paper: Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities: A Foundation for Design, Operation, and Patient Care Abstract: Healthcare facilities are complex environments designed to deliver a wide range of services. Effective classification of spaces within these facilities is crucial for optimizing design, ensuring regulatory compliance, promoting patient safety, and streamlining operations. This white paper explores the rationale, methodologies, and benefits of space classification in healthcare, highlighting best practices and emerging trends. 1. Introduction: Healthcare facilities, encompassing hospitals, clinics, ambulatory surgical centers, and long-term care facilities, are intricate ecosystems. Each space within these facilities serves a specific purpose, contributing to the overall patient care experience. A well-defined system for classifying these spaces is essential for various stakeholders, including architects, designers, healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, and, ultimately, patients. 2. Rationale for Space Classification: The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities serves several critical functions: 3. Methodologies for Space Classification: Several classification systems are employed in healthcare, often used in conjunction: 4. Best Practices in Space Classification: 5. Emerging Trends: 6. Conclusion: The classification of spaces in healthcare facilities is a fundamental process that underpins effective design, regulatory compliance, patient safety, and operational efficiency. By adhering to best practices and embracing emerging trends, healthcare providers can create environments that support the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered care. Continuous review and adaptation of space classifications are essential to ensure that healthcare facilities remain functional, safe, and responsive to the evolving needs of patients and the healthcare industry. Industrial application of Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities ? While the classification of spaces in healthcare facilities might seem like an abstract concept, it has significant industrial applications that impact various sectors: 1. Construction and Design: 2. Manufacturing and Supply Chain: 3. Technology and Software: 4. Consulting and Services: 5. Real Estate and Investment: In conclusion, the classification of spaces in healthcare
Classification of Spaces in Healthcare Facilities Read More »